Research Interests:
The cellular mechanisms underlying information processing leading to memory formation and learning is under intense debate. Research of our group focuses on the study of the mechanisms that regulate neural excitability and synaptic plasticity in the cerebral cortex and its role leaning and memory.
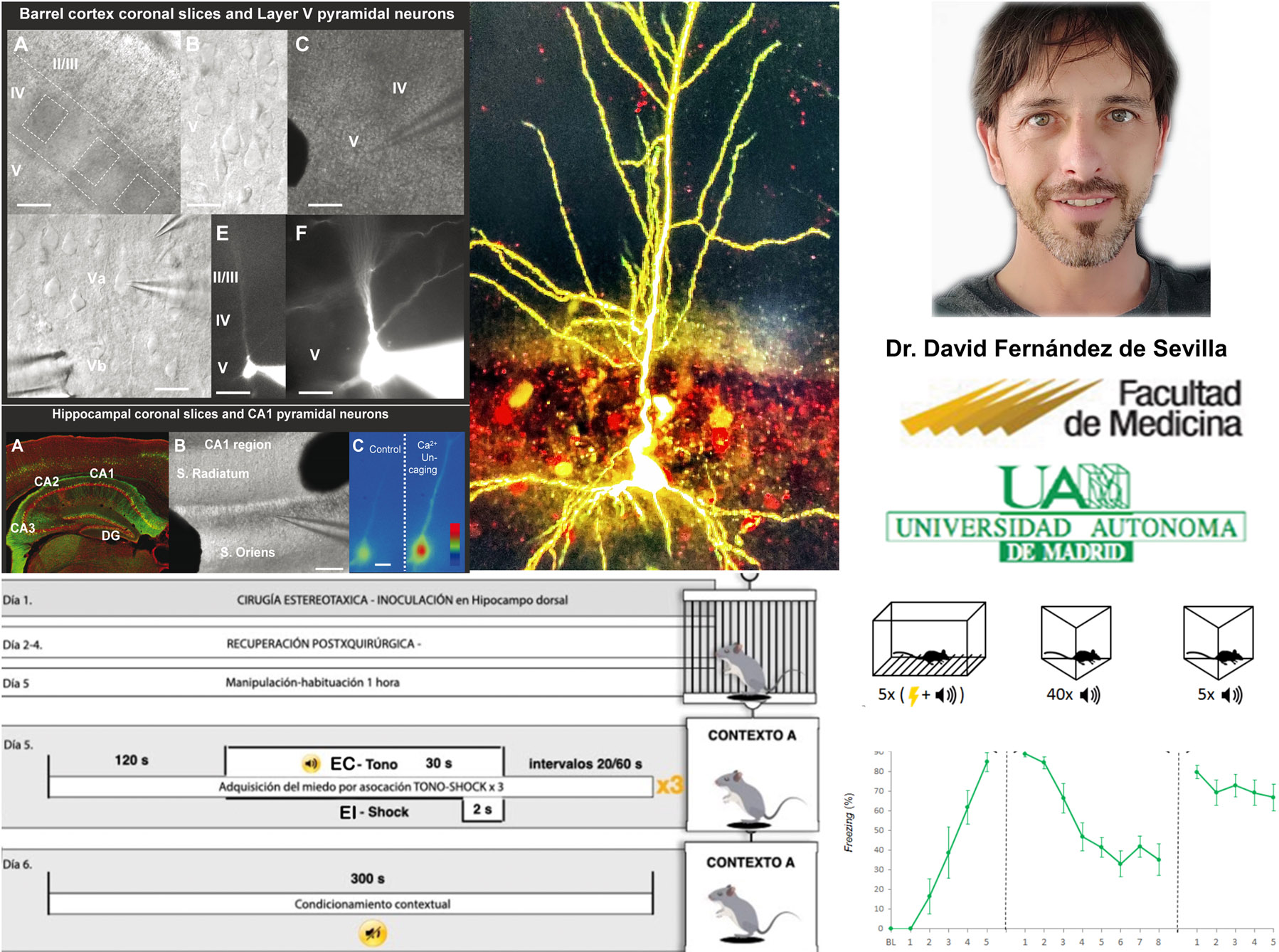
My previous work provided the demonstration that acetylcholine (ACh) is able to induce long term potentiation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission at CA1 pyramidal neurons of the hippocampus by increasing neuronal excitability and converting silent synapses into functional one through the insertion of glutamatergic AMPARs in its spines. Similarly we have proved that ACh is able to induce calcium spikes and potentiation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission at layer 5 pyramidal neurons of the barrel cortex.
Our current research lines aim to analyze:
- How endocannabinoids favor the induction of calcium spikes and its effect on excitability and synaptic plasticity in the somatosensory cortex.
- the mechanisms by which IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1) modulates synaptic transmission and neuronal excitability in the prefrontal cortex and its function in the fear conditioning memory.
- The role of astrocytes in the induction of synaptic plasticity required for the acquisition and maintenance of conditioned fear memories
Most relevant Techniques:
- Intracellular recording using the Patch clamp technique in rat or mouse brain slices.
- Extracellular recordings of the field potential in vitro and in vivo in the anesthesiated mice.
- Calcium imaging to monitor intracellular calcium activity of astrocytes and neurons.
- Optogenetics and chemogenetics.
- Fear conditioned Behavioural test.
- Surgery of rats and mice.
Past Lab Members, current employment
Andrea Díez García
Laura Maglio
Jose Antonio Noriega Prieto
Marta Callejo
Selected Publications
- Año: 2022
Noriega-Prieto JA, Maglio LE, Ibáñez-Santana S, Fernández de Sevilla D. (2022). Endocannabinoid and Nitric Oxide-Dependent IGF-I-Mediated Synaptic Plasticity at Mice Barrel Cortex. Cells.
- Año: 2021
Noriega-Prieto JA, Maglio LE, Zegarra-Valdivia JA, Pignatelli J, Fernandez AM, Martinez-Rachadell L, Fernandes J, Núñez Á, Araque A, Torres-Alemán I, Fernández de Sevilla D. (2021). Astrocytic IGF-IRs Induce Adenosine-Mediated Inhibitory Downregulation and Improve Sensory Discrimination. Journal of Neuroscience.
Maglio LE, Noriega-Prieto JA, Maroto IB, Martin-Cortecero J, Muñoz-Callejas A, Callejo-Móstoles M, Fernández de Sevilla D. (2021) IGF-1 facilitates extinction of conditioned fear. Elife.
Fernández de Sevilla D, Núñez A, Araque A, Buño W. (2021). Metabotropic Regulation of Synaptic Plasticity. Neuroscience.
Fernández de Sevilla D, Nuñez A and Buño W. (2021). Muscarinic Receptors, from Synaptic Plasticity to its Role in Network Activity. Cortex. Neuroscience.
- Año: 2019
Noriega-Prieto JA, Maglio LE, Gallero-Salas Y, Fernández de Sevilla D. (2019). Nitric Oxide-Dependent LTD at Infralimbic Cortex. Neuroscience.
- Año: 2018
Maglio LE, Noriega-Prieto JA, Maraver MJ, Fernández de Sevilla D. (2018) Endocannabinoid-Dependent Long-Term Potentiation of Synaptic Transmission at Rat Barrel Cortex. Cerebral Cortex.
- Año: 2017
Díez-García A, Barros-Zulaica N, Núñez Á, Buño W, Fernández de Sevilla D. (2017) Bidirectional Hebbian Plasticity Induced by Low-Frequency Stimulation in Basal Dendrites of Rat Barrel Cortex Layer 5 Pyramidal Neurons. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience.
Domínguez S, Fernández de Sevilla D, Buño W. (2017) Acetylcholine Facilitates a Depolarization-Induced Enhancement of Inhibition in Rat CA1 Pyramidal Neurons. Cerebral Cortex.